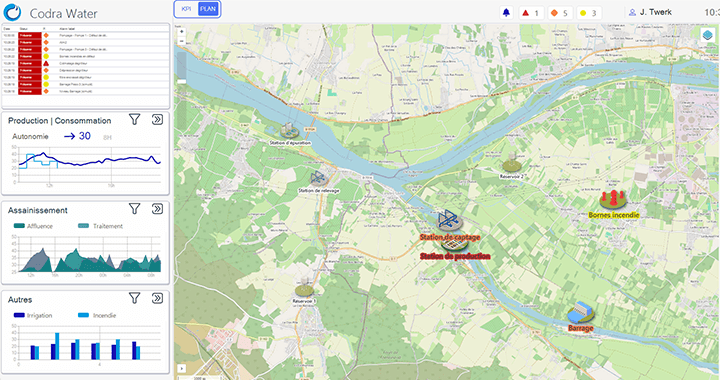
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play an essential role in modern SCADA. They enable geospatial data to be collected, analysed and visualised, facilitating more informed and effective decision-making.
Basic principles of Geographic Information Systems
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are powerful tools for managing spatial and geographic information. They enable all kinds of geo-referenced data to be captured, stored, manipulated, analysed, managed and presented. GIS offers a number of advantages, including :
- Accurate data collection: GIS integrates data from a variety of sources, including topographic surveys, satellite images and IoT sensors, to provide an accurate overview of the territory.
- In-depth analysis: with advanced spatial analysis capabilities, GIS helps to identify trends, predict future events and optimise resources.
- Clear visualisation: Interactive maps and 3D models generated by GIS make complex data easier to understand and improve communication between stakeholders.
By using GIS, managers can make more informed decisions and plan operations more effectively.
Geo-SCADA: GIS and SCADA interoperability
The integration of GIS with Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems enables more efficient and integrated SCADA. A Geo-SCADA combines the capabilities of GIS and SCADA to provide a unified platform for monitoring and managing complex infrastructures.
Benefits of a Geo-SCADA interoperability :
- Real-time visualisation – Geospatial data and real-time information from SCADA systems are merged to provide a dynamic visualisation of operations and infrastructure. To take this a step further, by combining GIS and BIM technologies, the operator has the opportunity to move towards multi-scale management of its application.
- Operations optimisation – The combined analysis of GIS and SCADA data enables more accurate planning and optimisation of operations, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Rapid incident response – Using geolocated, real-time data, operators can respond quickly and effectively to incidents, minimising any negative impact.
Integrated benefits of Geographic Information Systems for SCADA
GIS provides an integrated and dynamic view that is essential for effective and proactive infrastructure management. Visual and interactive data helps to better understand issues, optimise the use of resources and coordinate developments with operational and environmental needs.
- Proactive infrastructure management: GIS makes it possible to monitor the condition of infrastructure and plan preventive maintenance, thereby reducing the risk of breakdowns and repair costs.
- Enhanced security: By integrating geospatial data, managers can improve security by identifying areas at risk and developing appropriate prevention strategies. This GIS data can be integrated directly into an integrated SCADA solution.
- Sustainable development: GIS facilitates the planning and management of resources in line with the principles of sustainable development, helping to balance economic, social and environmental needs.
By integrating geographic information systems with SCADA solutions such as a Geo-SCADA, Codra offers an effective solution for infrastructure management and SCADA. This enables managers to make more informed decisions and maximize the efficiency of their operations. Adopting these advanced technologies represents an opportunity to radically transform the approach to SCADA.